Energy Monitoring Solution and Data Management
Energy Monitoring Solution and Data Management
GoSwitchgear provides IoT (Internet of Things) based energy monitoring and data management services that play a crucial role in optimizing energy usage, improving efficiency, and reducing costs for both residential and industrial applications. We provide and leverage IoT technologies, gateways, and energy meters to collect, analyze, and manage energy consumption data in real-time. Here’s an overview of the key components and functionalities:
Energy Monitoring projects in UAE
- Sensors and Energy Meters: Smart Meters: These devices measure energy consumption at a granular level and often provide real-time data. They are an essential part of IoT-based energy monitoring systems.
- Gateways: These devices act as intermediaries between the IoT devices (sensors, energy meters) and the cloud or central server. They collect data from the devices and transmit it securely to the central system. We provide GSM, Wi-Fi ( wireless) and Broadband ( Ethernet ) based gateways to pull the data and transmit to the cloud system.
- Communication Protocols implemented
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): A lightweight and efficient protocol for transmitting data between devices, commonly used in IoT applications.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): A protocol designed for resource-constrained devices and networks in IoT applications.
- Cloud-Based Platforms:
- Data Storage and Analytics: Cloud platforms also facilitate advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance and anomaly detection.
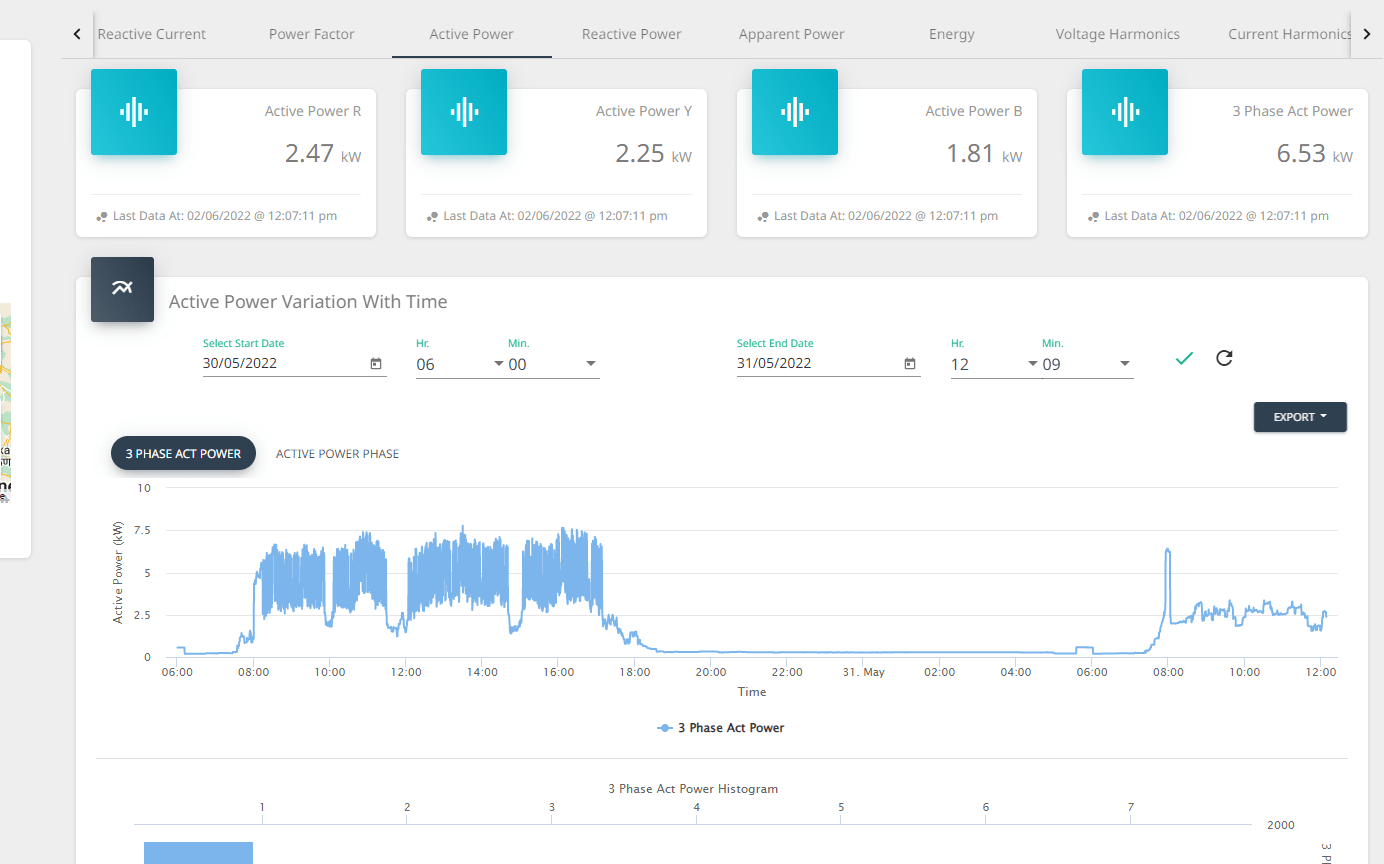
- Dashboard and Visualization: Users can access a user-friendly dashboard to monitor and analyze energy consumption in real-time. Visualization tools help in understanding patterns and identifying areas for improvement.
5. Remote Monitoring and Control: Users can remotely configure and manage connected devices, enabling real-time adjustments to optimize energy consumption.
6. Alerts and Notifications: Automated alerts are sent to users or administrators in case of abnormal energy consumption patterns, using Whatsapp, SMS and emails.
7. Energy Optimization: (i) Load Balancing: strategies to distribute energy usage more evenly, reducing peak demand and associated costs. (ii) Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and patterns, IoT-based systems can predict when equipment may require maintenance, preventing unexpected downtime.
8. Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS): Integration with BMS allows for holistic control of building systems, optimizing energy usage in alignment with other operational requirements.


