Solid State Relays: The Ultimate Guide for UAE & GCC Industries
For engineers, panel builders, and procurement teams in the UAE and GCC, specifying electrical components that withstand extreme heat, humidity, and dust is a constant challenge. Traditional electromechanical relays often fail under these conditions, leading to costly downtime. The solution is the solid state relay (SSR)—a modern, semiconductor-based switch with no moving parts, engineered for superior reliability in harsh environments.
Why Modern Industries in the UAE Need a Better Switch
In the high-stakes industrial landscape of the UAE and KSA, reliability is paramount. From manufacturing automation in Dubai to large-scale renewable energy projects across the GCC, component failure is not an option. Electromechanical relays (EMRs), with their moving parts and contact arcing, are susceptible to wear and tear, especially in the region's demanding climate. This has driven the need for a more robust switching technology.
The solid state relay directly addresses these pain points. By replacing mechanical contacts with durable semiconductor technology, an SSR can achieve a lifespan up to 100 times longer than a comparable EMR. This longevity translates to fewer maintenance cycles, lower replacement costs, and maximized uptime for critical systems.
The Growing Demand in the UAE and GCC
This technological shift is reflected in regional market trends. The Middle East's solid state relay market is poised for significant growth, fueled by major investments in infrastructure and renewable energy. An SSR's ability to handle rapid switching and operate flawlessly in high ambient temperatures makes it ideal for solar power installations and complex automated factories. For a deeper look, you can explore regional market analysis and growth projections for SSRs.
Key Advantages for Local Applications
For professionals working on projects in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and across the GCC, the practical benefits are clear:
- Silent Operation: The absence of moving parts means no audible "click," making SSRs ideal for noise-sensitive environments like control rooms or commercial buildings.
- No Electrical Arcing: SSRs switch electronically, eliminating arcs. This enhances safety and prevents the electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can disrupt PLCs and other sensitive electrical components UAE projects rely on.
- Superior Vibration Resistance: The solid-state design is inherently resistant to mechanical shock and vibration, a common issue near heavy machinery.
How a Solid State Relay Actually Works
To appreciate why a solid state relay is a superior choice for many industrial applications, it's essential to understand its internal operation. Unlike the mechanical action of an EMR, an SSR functions as a silent, light-activated switch, free from the wear and tear of moving parts.
The process begins when a low DC control voltage is applied to the relay's input terminals. This small current activates an internal light-emitting diode (LED). This LED emits an infrared light signal across a small physical gap within the relay's housing. This feature is the key to an SSR's complete electrical isolation, which safely separates the low-voltage control circuit from the high-power load circuit.
This diagram illustrates the elegant simplicity of the process.
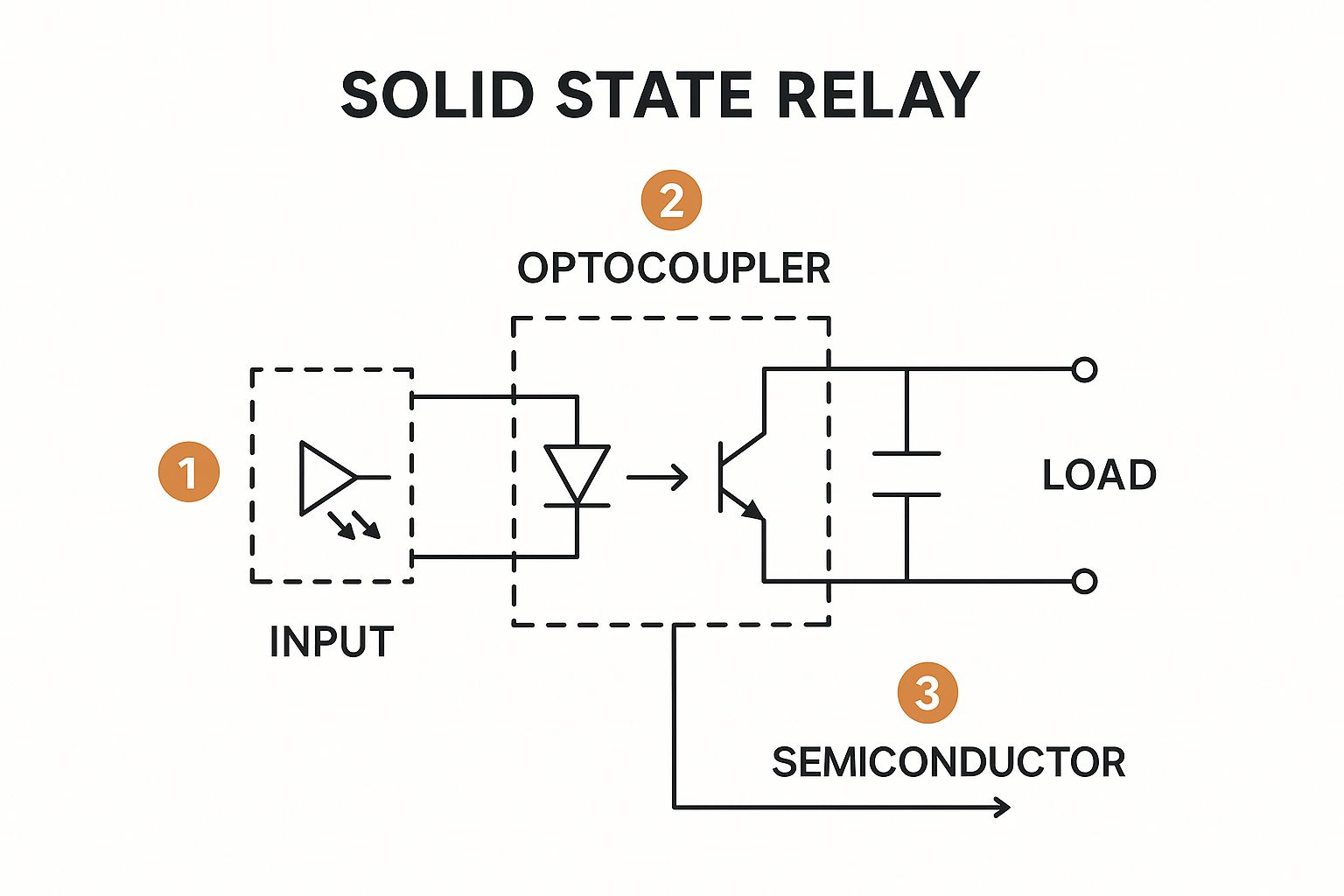
The input signal generates an optical signal that activates the power switch without any physical connection. A light-sensitive semiconductor, such as a photodiode, detects this infrared light on the other side of the gap.
Triggering the Power Switch
When the light hits the sensor, it "unlocks" the gate of the main power-switching semiconductor. This workhorse component is typically a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) for AC loads or a MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) for DC loads.
Once triggered, the semiconductor closes the circuit, allowing high-power current to flow to the connected load—be it a heater, motor, or lighting system. The entire process occurs in microseconds with no moving parts, no sparks, and no noise. While SSRs are masters of silent switching, comparing them to their mechanical counterparts is useful. You can learn more about how different types of general-purpose relays operate to fully grasp the technological advancement.
The opto-isolation inside an SSR not only protects sensitive control systems like PLCs from high-voltage transients but is also a primary reason for its incredibly long lifespan, often exceeding 50 million cycles.
Smart Switching for Different Loads
Modern SSRs are often more than simple on/off switches; they incorporate logic to manage different types of electrical loads, a critical feature for industrial use.
- Zero-Crossing Switching: Ideal for resistive loads like heating elements. The SSR intelligently waits for the AC voltage waveform to cross zero before switching. This minimizes electrical noise (EMI) and prevents interference with other equipment, a crucial aspect of any energy management solution Dubai requires.
- Random-Switching (Instant-On): Designed for inductive loads like motors and transformers. It switches the instant the control signal is received, providing the immediate power these components require.
SSR vs. Electromechanical Relay: A Practical Comparison for the GCC
When specifying components for a critical project, the choice between a solid state relay and an electromechanical relay (EMR) is a decision every engineer and procurement manager in the UAE must make. This involves balancing upfront cost against long-term performance and reliability.
While the lower initial price of an EMR can be appealing, the superior technology of an SSR often provides a much stronger ROI for demanding applications. The key differences become apparent when considering factors that directly impact uptime and safety, especially in the harsh operating conditions found across the energy meter GCC region and beyond.
Head-to-Head Feature Breakdown
To assist in making an informed decision, this side-by-side comparison highlights why SSRs are increasingly the preferred choice for modern, high-stakes applications where failure is not an option.
A key advantage of the solid state relay is its silent, arc-free switching. This is vital in control panels crowded with sensitive electronics, as it eliminates the EMI that can disrupt PLCs, a common issue with mechanical relays.
Here is a direct comparison of key characteristics between SSRs and EMRs to guide your selection for industrial applications in the UAE.
Solid State Relay vs. Electromechanical Relay: A Comparison
| Feature | Solid State Relay (SSR) | Electromechanical Relay (EMR) |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Lifespan | 50-100+ million cycles. No moving parts, no mechanical wear. | 100,000 to 1 million cycles. Physical contacts degrade over time. |
| Switching Speed | Extremely fast (microseconds). | Slower (milliseconds). |
| Electrical Noise (EMI) | Very low to none (especially zero-crossing models). | Generates significant EMI from contact arcing. |
| Shock & Vibration Resistance | Excellent due to solid, potted construction. | Poor; moving parts are susceptible to shock. |
| Control Power Consumption | Very low. | Higher power needed to energize the coil. |
| Audible Noise | Completely silent. | Produces an audible "click." |
| Heat Dissipation | Requires a heat sink for high-current loads. | Generates less heat per amp. |
Justifying the Investment in the UAE Climate
Yes, the initial purchase price of an SSR is higher. However, the total cost of ownership is often significantly lower. An SSR's lifespan, often over 100 times that of an EMR, drastically reduces replacement and labor costs. This is particularly true for applications with high switching frequencies, such as temperature control systems using a SMPS power supply or PWM.
For critical infrastructure projects in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, the enhanced reliability, silent operation, and long service life of an SSR are essential for protecting system integrity.
How to Select the Right Solid State Relay for Your Application
Choosing the correct solid state relay goes beyond matching voltage and current. For engineers and panel builders in the UAE, a successful specification hinges on understanding the load, switching requirements, and local operating conditions.
The first step is identifying your load type: AC or DC. For AC loads like heaters and motors, you need an SSR with a TRIAC or SCR output. For DC loads such as solenoids, a model with a MOSFET or IGBT output is required.
Key Selection Criteria for UAE and GCC Projects
To prevent premature failure, especially in the GCC's climate, you must consider these critical factors:
- Switching Method: As discussed, zero-crossing SSRs are ideal for resistive loads, minimizing EMI. Random or instant-on SSRs are necessary for inductive loads like motors that require immediate power.
- Mounting Style: Panel-mount SSRs are bolted directly to a heat sink, ideal for high-current applications. DIN rail isolator style SSRs are popular for control cabinets due to their quick, tool-free installation. PCB-mount versions are available for compact designs.
- Environmental Protection (IP Rating): In the dust and humidity of the GCC, the IP rating is crucial. An IP20 rating is sufficient for relays inside a sealed control panel. For more exposed locations, a higher IP rating is necessary to ensure longevity and compliance with local standards.
A Critical Focus on Thermal Management
Thermal management is the single most critical factor for an SSR's survival in a hot climate. An SSR generates approximately 1 to 1.5 watts of heat per ampere of switched current. Without proper heat dissipation, the relay will fail.
In high-temperature environments like Dubai and Saudi Arabia, selecting an adequate heat sink is not optional; it is essential for reliability. Failure to account for ambient temperature is a leading cause of SSR failure in the field.
Calculating thermal resistance and choosing the right heat sink is a core engineering task. It involves considering the maximum ambient temperature, load current, and thermal resistance values from the SSR's datasheet. For a detailed guide on choosing protective components, see our article on selecting the right electrical protection relays.
Installation Best Practices and Common Mistakes to Avoid
Proper installation ensures a solid state relay delivers its promised longevity and reliability. For electricians and panel builders in the UAE, following best practices is critical to preventing premature failures and costly downtime.
The process begins with clean, secure connections. Ensure all terminal screws are tightened to the manufacturer's specified torque. A loose connection creates resistance and a hot spot that can damage the relay.
Always use the correct wire gauge for the current load. Undersized wires are a fire hazard and can lead to performance issues.
How to Install an SSR: Essential Steps
- Mount on a Flat Surface: The SSR base must be flush with the heat sink or panel. Gaps will impede heat transfer and cause overheating.
- Use Thermal Compound: Apply a thin, even layer of thermal paste between the SSR and heat sink to ensure optimal heat transfer.
- Ensure Proper Airflow: Even with a heat sink, an SSR needs ventilation. In crowded or high-temperature panels, a fan may be necessary.
- Verify Control Voltage: Double-check that the control voltage from your PLC or controller matches the SSR's rating to prevent damage.
Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
Most SSR failures are due to preventable installation errors.
A common mistake is failing to derate the SSR's current capacity for ambient temperatures above 25°C. In the GCC, this is a direct path to thermal overload and failure.
- Forgetting Overcurrent Protection: SSRs have low tolerance for short circuits. Protect them with a fast-acting fuse (Type gR or aR) or a semiconductor-specific circuit breaker. Standard breakers are too slow.
- Mismatched Load Type: Using a zero-crossing SSR for a highly inductive load will lead to failure. Match the SSR's switching type to the load.
- Incorrect Wiring: Reversing the line and load connections will instantly destroy the SSR.
Troubleshooting Common Solid State Relay Problems
https://www.youtube.com/embed/qIeZR7TuYxo
Even a properly installed solid state relay can encounter issues. Knowing how to quickly diagnose problems is key to minimizing downtime. SSRs typically fail in one of three ways: failure to turn on, failure to turn off, or overheating.
Problem: The Relay Will Not Turn On
If the load remains off when a control signal is applied, start with these checks:
- Check Control Voltage: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the SSR's input terminals. Ensure it is within the specified range (e.g., 3-32 VDC).
- Verify Load Circuit: Check for blown fuses, tripped breakers, or broken wires in the load circuit.
- Confirm Connections: Ensure all input and output wires are securely fastened.
Problem: The Relay Will Not Turn Off
This dangerous situation, where the relay is "stuck on," almost always indicates an internal failure of the semiconductor, usually caused by a severe overcurrent or short circuit that has fused the switch. If you suspect this, our guide on how to test a relay provides a safe diagnostic procedure.
Another less common cause is leakage current. All SSRs allow a minuscule current to pass in the "off" state. For very low-power loads, this leakage might be enough to cause a faint glow.
Your Partner for Reliable Switching Solutions in the UAE
The solid state relay is the superior switching technology for the industrial, commercial, and renewable energy sectors in the demanding climate of the UAE and GCC. Its reliability, long lifespan, and silent operation make it a strategic investment for any modern system.
As this guide has shown, careful selection based on load type, switching needs, and proper installation with a focus on thermal management are non-negotiable for success in high-temperature environments.
Choosing a solid state relay is an investment in your system's stability and operational excellence, minimizing future maintenance and maximizing uptime.
For expert guidance on your next project, the GoSwitchgear team is ready to assist. We support engineers, procurement managers, and panel builders across Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and the wider GCC with technical expertise and a portfolio of high-quality electrical components UAE industries trust.
Reach our Dubai team for project support or explore our full range of electrical components at GoSwitchgear.









Leave a Reply