A Guide to Selecting the Right Electrical Cable Lugs Types for the GCC Climate
In any reliable electrical system, from a high-rise in Dubai to an industrial plant in Saudi Arabia, electrical cable lugs are the critical handshake between a cable and its terminal. Choosing the right lug isn't just about a good connection; it's about guaranteeing safety, durability, and compliance in the demanding GCC climate.
Choosing the Right Lug for Your Electrical System
This guide will walk you through the essential electrical cable lugs types, covering materials, shapes, and applications. We'll explore how to match the perfect lug to your project—whether it's a massive industrial build or a residential panel—to ensure your electrical systems are both rock-solid and efficient in the face of local challenges like heat, humidity, and dust.
Think about any electrical installation, from complex control panels to high-voltage switchgear. The termination point is almost always the weakest link. A poorly chosen or badly installed lug can cause serious problems, like increased resistance, dangerous overheating, and eventual system failure. These are risks you cannot afford in the demanding operational environments of the UAE and KSA.
In a region where temperatures routinely soar past 45°C, the thermal performance of an electrical connection is paramount. The right lug ensures minimal power loss and heat generation, which is a direct line to system stability and safety.
Understanding the Core Function of a Lug
At its heart, a cable lug has two main jobs:
- Mechanical Strength: It provides a tough, secure anchor for the cable. This prevents it from being pulled loose by vibrations or physical tension, which is crucial for industrial machinery and transport applications.
- Electrical Conductivity: It creates a reliable, low-resistance path for electricity to flow from the cable's conductor to the terminal. This ensures top efficiency and prevents hazardous hot spots from forming.
Making the right choice goes beyond just matching wire sizes. You need a solid grasp of material properties, application demands, and local compliance standards. To better understand their crucial function, you can learn more about the role of cable lugs in control panel systems and see how they uphold system integrity. This foundational knowledge is key to building safe and dependable electrical infrastructure anywhere in the UAE.
Understanding Core Lug Materials: Copper vs. Aluminium
The material you choose for an electrical cable lug is the foundation of its performance, dictating conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. When working on any project in the UAE and the wider GCC, selecting the right material is a critical decision that directly impacts long-term safety and reliability under harsh local conditions.
Two materials dominate the cable lug market: copper and aluminium. Each has distinct properties suited for specific applications. An incorrect choice can lead to inefficient power flow, dangerous overheating, or connection failure from corrosion—a significant risk in the Gulf's climate, where heat and saline humidity stress all electrical components UAE projects.
The Gold Standard: Copper Lugs
When performance and reliability are non-negotiable, copper is the premium choice for electrical cable lugs.
Its primary advantage is exceptional electrical conductivity, second only to silver. In practical terms, this means lower electrical resistance, resulting in less energy waste and minimal heat buildup at the connection point. This is a massive benefit for high-power systems and a crucial safety factor in the hot GCC climate.
Copper is also mechanically tough and ductile, meaning it can withstand the immense pressure of crimping without cracking and resist vibrations and mechanical stress over its lifespan. This ensures a solid, dependable connection that lasts.
This makes copper the only viable choice for critical applications like:
- High-current switchgear in industrial plants and data centers.
- Power distribution units in commercial towers across Dubai and Abu Dhabi.
- Motor terminations where constant vibration and temperature fluctuations are standard.
To combat corrosion in the humid, salty air common along the UAE coast, high-quality copper lugs are almost always tin-plated. This layer acts as a protective shield, preventing oxidation and ensuring a stable, low-resistance connection for years.
The Lightweight Contender: Aluminium Lugs
Aluminium is a compelling alternative to copper, primarily due to its significantly lower weight and cost. An aluminium lug is approximately one-third the weight of a comparable copper one.
This weight reduction is a game-changer for large-scale projects like long-distance overhead power lines or extensive busbar systems. It simplifies handling and installation, making it a more budget-friendly option, especially when large quantities of cables and lugs are required.
While aluminium's conductivity is only about 60% that of copper, it excels in its conductivity-to-weight ratio, making it a highly efficient choice where minimizing weight is a top priority.
However, aluminium has specific requirements. It is a softer metal and rapidly forms a resistive oxide layer on its surface. To overcome this, aluminium lugs are pre-filled with an oxide-inhibiting compound that breaks down this insulating layer during crimping, ensuring a clean and reliable electrical connection.
Technical Comparison of Copper and Aluminium Lugs for GCC Projects
When deciding between copper and aluminium for a project in the Gulf, a side-by-side technical comparison is invaluable. The region's climate and regulations place unique demands on electrical components, so understanding how these materials perform in this specific environment is key to a safe and cost-effective choice.
| Parameter | Copper Lugs | Aluminium Lugs | Best Use Case in UAE/GCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent (100% IACS). Minimizes heat and energy loss. | Good (61% IACS). Higher resistance requires a larger conductor for the same ampacity. | Copper: High-current switchgear, data centers, and critical infrastructure where efficiency is paramount. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, but requires tin plating (high IP rating) in coastal/humid areas to prevent oxidation. | Fair. Rapidly forms a non-conductive oxide layer. Requires inhibiting compound and proper surface preparation. | Copper (tin-plated): Ideal for coastal projects in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah. Aluminium: Best for inland, dry areas where saline humidity is less of a concern. |
| Mechanical Strength & Durability | High. Withstands high crimping pressure and vibration without fatigue. | Lower. Softer material, more prone to creep and loosening under thermal cycling. | Copper: Perfect for motor terminations, generators, and heavy machinery with constant vibration. |
| Weight | Heavy (Density: 8.96 g/cm³). | Lightweight (Density: 2.7 g/cm³). About 1/3 the weight of copper. | Aluminium: Excellent for long-run overhead power lines and large-scale residential/commercial wiring where structural load is a factor. |
| Cost | Higher initial material cost. | Significantly Lower initial material cost. | Aluminium: Budget-sensitive projects like mass housing or commercial builds where material volume is high. |
| Termination Complexity | Straightforward. Easy to crimp, providing a reliable connection. | More Complex. Requires inhibiting grease and careful wire brushing to ensure a good, long-lasting connection. | Copper: Applications where speed and ease of installation are critical for project timelines. |
In summary, while copper offers unmatched performance for critical, high-power applications, aluminium provides a cost-effective and lightweight solution for large-scale distribution, provided its specific installation requirements are met.
The Essential Bridge: Bi-Metallic Lugs
What happens when you need to connect an aluminium cable to a copper busbar? Connecting these two dissimilar metals directly is a classic and dangerous mistake. It creates the perfect conditions for galvanic corrosion—an electrochemical reaction that degrades the connection, eventually causing failure and creating a serious fire risk.
This is where a bi-metallic lug comes in. It is engineered specifically to solve this problem, featuring an aluminium barrel that is friction-welded to a copper palm.
This design creates a safe, stable bridge between aluminium and copper conductors, eliminating the risk of galvanic corrosion. It is an absolute must-have for countless upgrades and new construction projects within the energy management solution Dubai sector.
Market trends support this. Copper's durability keeps it at the forefront for power infrastructure expansion, while aluminium's cost-effectiveness makes it popular for residential and commercial construction. As safety standards across the UAE become stricter, demand for insulated and pre-insulated lugs continues to rise, especially for harsh industrial settings. For a deeper dive, a detailed analysis of the electrical cable lugs market to understand these trends is available.
A Practical Guide to Lug Shapes and Barrel Designs
After selecting the material, the lug's physical design is the next critical consideration. The shape of the lug's palm and the design of its barrel dictate its specific application. Using the wrong design is like using a screwdriver to hammer a nail—it simply won't work correctly.
The lug's physical form is engineered for specific connection points and environments. This makes choosing the right shape a make-or-break decision when selecting from the various electrical cable lugs types. It’s not just about what fits; it’s about creating a connection that is mechanically solid and electrically sound for the long term. For any electrician or panel builder in the UAE, matching the lug's shape to the terminal is fundamental for a safe, compliant installation.
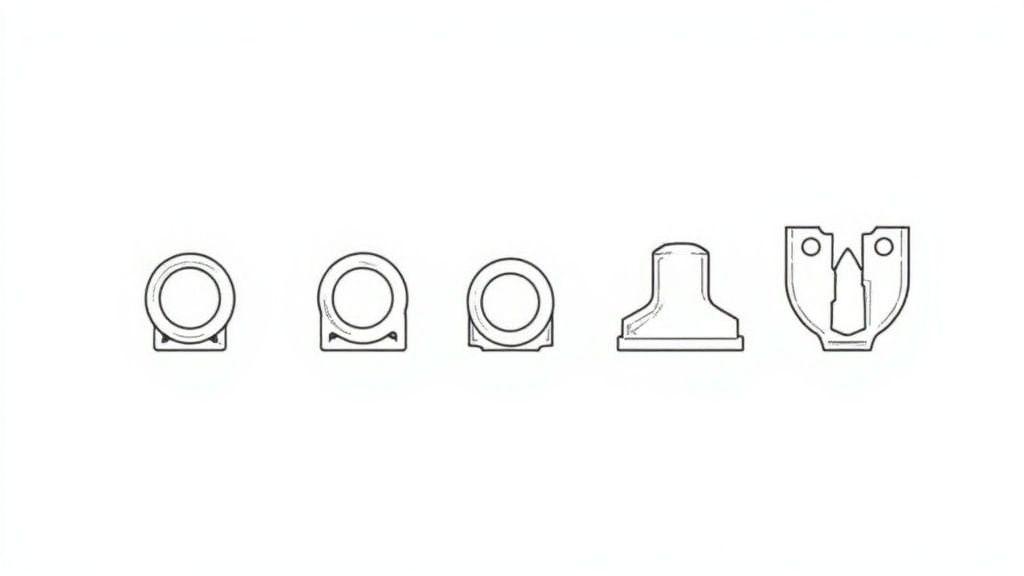
Common Lug Shapes for Every Task
The palm of the lug comes in several standard shapes, each offering a trade-off between installation speed and connection security.
-
Ring Lugs: These are the most secure and common shape. The closed-loop design wraps completely around the stud or bolt, meaning the lug cannot slip off even if the fastener loosens due to vibration. This makes ring lugs the standard for critical connections in switchgear, motors, and transformers.
-
Fork (or Spade) Lugs: With a U-shaped opening, these lugs can be installed or removed by simply loosening the terminal screw instead of removing it completely. This is a significant time-saver in crowded control panels. The trade-off is reduced security against vibration compared to ring lugs.
-
Pin Lugs: These lugs provide a neat solution for terminating stranded wires into screw-type terminal blocks designed for solid conductors. The solid pin gathers all the fine strands, preventing any from straying and causing a short circuit, ensuring a clean, reliable connection in PLC wiring and certain circuit breakers.
Standard vs. Long Barrel Designs
The barrel is the part of the lug crimped onto the cable. Its length is surprisingly important, affecting both the mechanical strength and electrical performance of the connection.
Key Insight: A longer barrel provides more surface area for the crimp, creating a stronger physical grip on the conductor and improving electrical conductivity.
This leads to two main barrel types:
-
Standard Barrel Lugs: These are the workhorses for most general-purpose applications. They provide a solid crimp with sufficient mechanical strength for typical wiring in control panels, lighting circuits, and residential distribution boards. Their compact size is also advantageous in tight spaces.
-
Long Barrel Lugs: The extended barrel on these lugs allows for two or more crimps, dramatically increasing the connection's tensile strength and electrical contact area. This makes them the go-to choice for heavy-duty applications common in the GCC's industrial and transport sectors.
Consider using long barrel lugs for:
- High-vibration areas like generators or heavy machinery.
- High-current applications where maximum conductivity is needed to minimize heat.
- Installations where the cable may be under mechanical tension.
For any project in Dubai or across the GCC, considering physical stresses is as crucial as the electrical load. Choosing a long barrel lug in a demanding environment is a simple step that adds significant security and longevity to your electrical components UAE systems.
Why Proper Crimping and Termination Are Critical
You can select the perfect lug, but it is useless if not installed correctly. The crimping process is the non-negotiable step that creates a permanent, reliable bond between the cable and the lug.
A proper crimp forges a connection that is both mechanically tough and electrically perfect. This bond must withstand constant vibrations and physical stress, a daily reality in industrial and transport sectors across the UAE. Electrically, it must create a seamless, low-resistance path for current, preventing dangerous overheating and ensuring system efficiency.
For any professional in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, or the wider GCC, mastering this process is a mark of quality. A bad termination is not a minor mistake; it can lead to catastrophic equipment failure, costly downtime, and serious safety hazards.
Understanding Crimping Methods and Tools
Crimping deforms the lug’s barrel and the cable’s conductors into a single, solid mass. This requires specialized tools that apply precise force. Using pliers or a hammer is a recipe for disaster, creating weak connections guaranteed to fail.
Two primary crimping methods are standard in the industry:
- Hexagonal Crimp: This is the go-to method for power cables. It applies even, symmetrical pressure, creating a strong hexagonal shape. This provides excellent electrical contact and mechanical strength, making it ideal for the larger electrical cable lugs types used in switchgear and power distribution.
- Indent Crimp: This method uses a die to press an indent into the lug barrel. It is often used for smaller terminals and is effective but creates a more concentrated point of pressure compared to a hexagonal crimp.
The golden rule is simple: always use the crimping tool and die set specified by the lug manufacturer. This is the only way to ensure the crimp has the correct force and shape for that specific lug and cable size, guaranteeing a reliable termination.
Common Crimping Mistakes to Avoid
A poor crimp introduces a hidden, ticking time bomb into your system. Getting the termination right is critical everywhere, from massive industrial machines to the connections for wired security cameras.
Here are the most common installation mistakes every electrician must avoid:
- Under-Crimping: Insufficient force or a die that is too large leaves gaps between the conductor and the lug barrel. These gaps trap air and moisture, leading to oxidation, higher resistance, and dangerous overheating.
- Over-Crimping: Excessive force or a die that is too small can crush the lug barrel, damaging conductor strands, weakening mechanical strength, and potentially causing the lug to crack under load.
- Incorrect Lug/Cable Combination: Forcing a lug onto a mismatched cable size is a fundamental error that will always result in a bad connection. Always double-check that the lug is rated for the specific cable class and cross-sectional area.
A Perfect Crimp: The Gas-Tight Connection
The ultimate goal of crimping is to create a "gas-tight" connection. This means the process has squeezed out all air pockets between the conductors and the lug. This cold weld prevents oxygen and moisture ingress, stopping corrosion and ensuring a stable, low-resistance connection for life.
Compliance with International Standards
For any major project in the UAE and KSA, following international standards like IEC 61238-1 is often a contractual obligation. This standard outlines strict testing for mechanical strength and electrical stability to prove that a specific lug, tool, and cable combination will perform reliably. Using IEC-compliant components from a trusted supplier like GoSwitchgear provides verifiable proof that your termination is safe and built to last. Equally important is the insulation around these connections; our guide on insulation materials for electrical applications ensures every part of your system is protected.
Navigating Insulated and Specialized Lug Types
While a lug's core function is creating a solid connection, some situations demand extra protection or specialized designs. In busy control panels, commercial electrical rooms, or high-density enclosures across the UAE, safety and clarity are critical. This is where insulated and other specialized electrical cable lugs types are essential.

These advanced lugs are engineered to prevent accidental contact, simplify wire identification, and solve complex termination challenges. Their role is vital in modern electrical systems, ensuring both personnel safety and system integrity where failure is not an option.
The Critical Role of Pre-Insulated Lugs
Pre-insulated lugs are an everyday workhorse for electricians and panel builders. They come with a tough insulating sleeve, typically made of PVC or nylon, already fitted over the barrel. This simple feature offers several powerful benefits.
- Enhanced Safety: The insulation sleeve covers the entire crimped barrel, drastically reducing the risk of accidental contact with live parts in a cramped panel or junction box.
- Simplified Identification: The insulation is color-coded according to a standard system. Each color corresponds to a specific wire size range (e.g., red for smaller gauges, blue for medium, yellow for larger), speeding up work and preventing mistakes.
- Vibration Resistance: The snug-fitting sleeve provides extra strain relief, helping to protect the connection from damage caused by vibrations over time.
Given the GCC's climate, the quality of this insulation is critical. The materials must be rated for high ambient temperatures to avoid becoming brittle. A high-quality nylon sleeve, for example, will withstand heat much better than standard PVC.
Non-Insulated Lugs for High-Power Applications
Non-insulated lugs are bare metal lugs used in applications where external insulation, like heat shrink tubing or insulating boots, will be applied after crimping.
These are the go-to choice for high-voltage switchgear, large motor terminations, and power generation facilities. In these heavy-duty environments, connections often require more robust, higher-rated insulation than a simple pre-fitted sleeve can provide. Using non-insulated lugs gives engineers the flexibility to apply custom insulation matched to the project's specific voltage and environmental stresses.
Specialized Lugs for Unique Challenges
Beyond insulated vs. non-insulated, a world of specialized lugs exists to solve specific wiring problems.
Expert Insight: Choosing the right lug often involves a trade-off between installation speed and long-term reliability. A pre-insulated fork lug is quick and easy, but a heavy-duty, non-insulated ring lug offers maximum security for critical infrastructure.
Here are key examples:
- C-Taps: These C-shaped connectors are perfect for making a secure, permanent tap from a main conductor without cutting it, enabling parallel connections in tight spaces.
- Heavy-Duty Lugs: Built with thicker walls and often longer barrels, these lugs are engineered for the largest cable sizes to withstand the immense forces in utility-scale power grids and major industrial projects across Dubai. Getting the size right is crucial; our detailed cable gland size chart helps ensure your entire termination system is specified correctly.
How to Select the Right Lug for Any Application
Selecting the right lug is a critical decision, not a guessing game. For engineers, procurement teams, and electricians in the UAE, getting this right is essential for safety, compliance, and long-term reliability. A single mistake can compromise an entire electrical system.
This practical checklist will help you navigate the vast range of electrical cable lugs types and confidently choose the perfect one for your application.
This infographic breaks down the initial decision-making process based on critical factors like cable size, environment, and connection type.
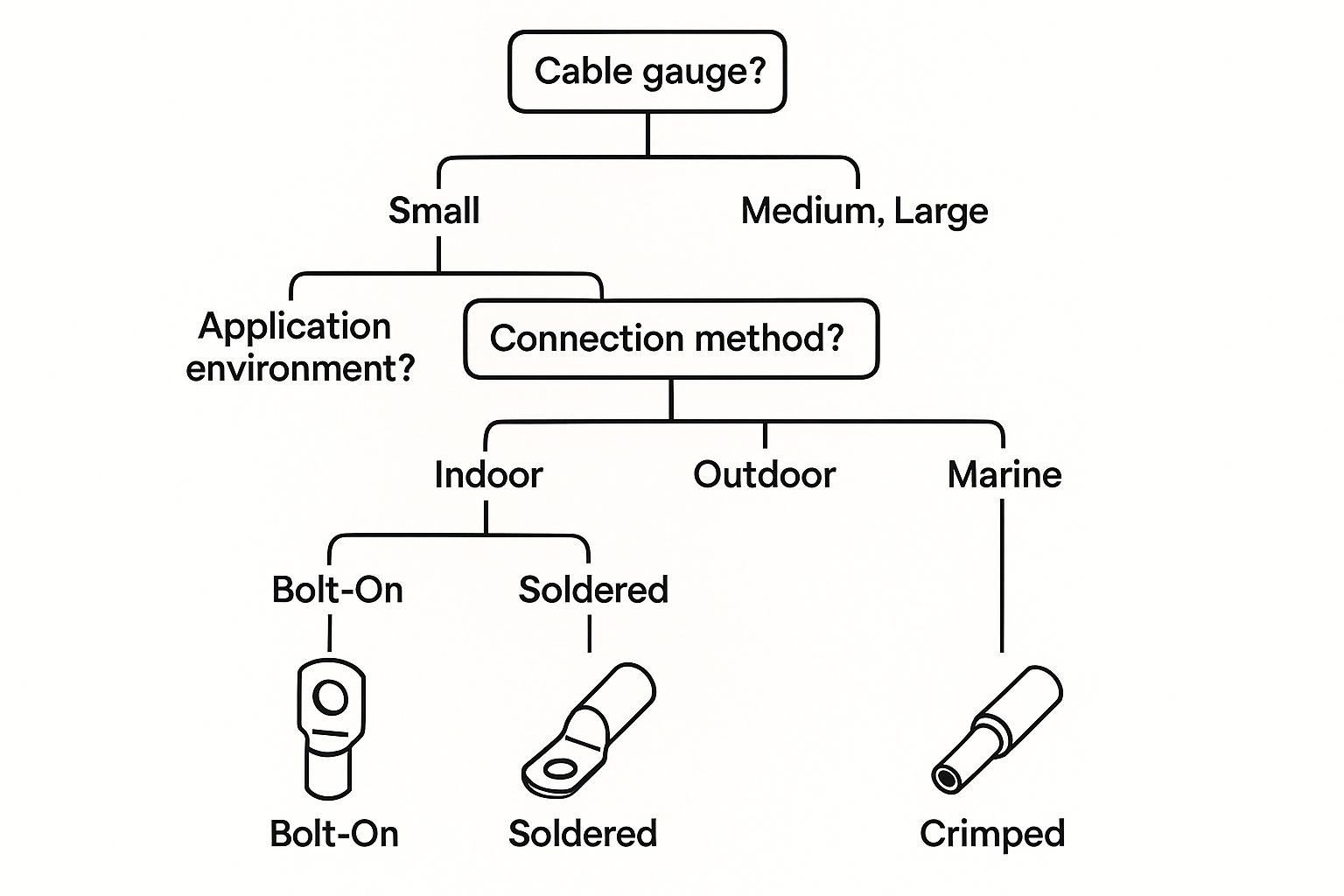
As you can see, the path to the right lug depends heavily on whether the application is indoors, outdoors, or in a harsh marine environment.
The Five-Point Selection Checklist
Follow these five steps to specify the correct lug every time, preventing costly mistakes and protecting your project's integrity.
1. Conductor Size and Type
This is the starting point. The lug must perfectly match the cable's cross-sectional area (mm² or AWG) and conductor type (stranded or solid). A mismatched lug creates a weak crimp, leading to overheating and failure. Always check the manufacturer's datasheet to confirm compatibility.
2. Voltage and Current Rating
The lug must handle the electrical load. Its voltage and current ratings must meet or exceed the system's demands. An underrated lug is a major safety hazard. For high-current applications, heavy-duty or long-barrel lugs are almost always necessary.
3. Termination Point Specifications
Where is the lug being connected? The hole in the lug's palm must match the stud or bolt size on the terminal block or busbar. An oversized hole creates a loose connection; an undersized one won't fit. Match the palm shape—ring, fork, or pin—to the terminal type for a secure fit.
4. Environmental and Operating Conditions
The UAE's climate of intense heat, humidity, and dust directly influences your choice of material and plating.
- For high humidity and coastal areas (Dubai, Abu Dhabi): Tin-plated copper lugs are non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure a stable connection.
- For high-temperature environments: Use lugs made from materials with a high melting point and ensure any insulation is also rated for high temperatures.
- For high-vibration applications (generators, heavy machinery): Choose long-barrel ring lugs for maximum mechanical strength.
5. Regulatory and Standards Compliance
For any project in the GCC, adherence to local and international standards is mandatory. Ensure your chosen lugs comply with key standards like IEC 61238-1. Additionally, components connected to the main grid must meet the requirements of local authorities like DEWA. Using compliant products from a trusted supplier like GoSwitchgear is critical for project approval.
This careful selection process is more important than ever. The Middle East's cable lug market is booming, driven by massive construction growth. With Saudi Arabia alone managing projects valued at around USD 819 billion, the need for dependable electrical connections is skyrocketing.
Common Questions About Cable Lugs
Here are answers to common questions from electricians and engineers in the region. Getting these details right is crucial for a safe, reliable, and compliant installation.
Why Is Tin-Plating on Copper Lugs So Important in the GCC?
Tin-plating is essential armor for copper lugs in this region. The GCC's high humidity and salty air, especially in coastal hubs like Dubai, are aggressive toward bare copper. Oxidation can form quickly, creating a poor connection that overheats and fails.
Tin forms a tough, non-corrosive barrier that shields the copper, ensuring a solid, low-resistance connection that lasts. It also prevents galvanic corrosion when connecting to aluminum busbars.
Can I Use an Aluminum Lug on a Copper Cable?
Absolutely not. This is a critical safety rule. Connecting an aluminum lug directly to a copper cable creates a bimetallic junction. The moment moisture is present—inevitable in our climate—galvanic corrosion begins, aggressively eating away at the connection, causing resistance to spike and creating a serious fire hazard. The only safe way to join copper and aluminum is with a specially designed bi-metallic lug.
What Happens If I Use the Wrong Crimping Die Size?
Using the wrong die guarantees a failed connection, even if it looks acceptable externally.
If the die is too big, you'll under-crimp the lug, leaving gaps that trap moisture and lead to overheating under load. If the die is too small, you'll over-crimp it, crushing conductor strands and weakening the lug barrel, making it brittle and prone to cracking. Always use the exact die size recommended by the lug manufacturer.
What Do the Colors on Pre-Insulated Lugs Mean?
The colors on pre-insulated lugs are a standardized visual code that instantly identifies the wire size range the lug is designed for, speeding up work and preventing mistakes.
While there can be slight variations, the general code is:
- Red: For smaller wires, typically 0.5-1.5 mm²
- Blue: For mid-range wires, like 1.5-2.5 mm²
- Yellow: For larger wires, often in the 4-6 mm² range
While this system is handy, always double-check the manufacturer’s datasheet to be 100% certain of the match.










Leave a Reply